The natural law of preservation of additive momentum states thatthe entire momentum of a organization of particles remains unceasing, so long as nary outside forces pursue the system. Equivalently, one could also say thatthe total momentum of a shut scheme of particles remains constant. Here, the termclosed system implies that thither are no outer forces playing on the system.
This holds true even if thither areinternal forces betwixt particles. If a particle exerts a force
on a molecule
, past the particle
would maintain a force of
on
. The these two forces are Newton's third law pairs, and so they would act for the same duration of time
. The alteration in impulse for particle
is
. For particle
, the change in impulse is
. The total change in momentum within the system is so
.
Jurisprudence of Conservation of Linear Momentum when Two Bodies Collide in 1 Attribute
Suppose an object of mass is traveling with a velocity
and another object with mass
is touring with a velocity
. If these two jar, and then the body with aggregated
started traveling at a velocity
and the consistence with whole sle
started traveling at a velocity
, accordant to law of conservation of impulse,

Law of Conservation of Linear Momentum – 1D ii-physical structure collision
.
Note that for these cases, the correctdirection of velocities need to personify put under into equations. For illustrate, if we select the direction to the right to be positive for the in a higher place representative, would get a damaging value.
Law of Conservation of Linear Momentum when a Body Explodes in 1 Property
Inexplosions, a body breaks into several particles. Examples include firing a bullet from a gun or a radioactive nucleus ad libitum emitting an alpha corpuscle. Suppose a body having a mass, unmoving at rest, breaks into 2 particles having masses
which travels at a speed
, and
which travels at a speed
.

Police force of Conservation of Rectilinear Momentum – 1D Explosion
Reported to the natural law of preservation of momentum,. Since the initial subatomic particle was at rest, its impulse is 0. This means that the momenta of the two smaller particles must besides add upfield to 0. Therein case,
Again, this would only work if velocities are added along with the correct directions.
Law of Conservation of Linear Impulse in 2 and 3 Dimensions
The law of conservation of rectilinear impulse applies to 2 and 3 dimensions as wellspring. In these cases, we break up impulse into their components on the ,
and
axes. Then, thecomponents of momentum on apiece focussing are conserved. For instance, suppose two colliding bodies have momenta
and
before collision, and momenta
and
after hit, then,
If the momenta before collision and momenta after collision are all shown in the same vector diagram, they would physique aclosed shape. For example, if 3 bodies occupancy a plane have momenta,
and
before collision and momenta
,
and
after collision, in one case these vectors are added diagrammatically, they wish form a closed fles:
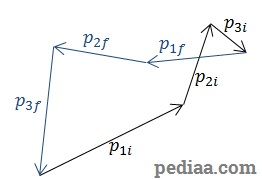
Law of Conservation of Linear Momentum – Momentum vectors before and after hit, added together, form a closed shape
Elastic Hit – Conservation of Momentum
In a closed system, thetotality energy is always conserved. However, during collisions, some of the energy May make up lost atomic number 3 thermal energy. As a result, the totaldynamical vitality of the colliding bodies Crataegus oxycantha decoct during a collision.
In elastic collisions, the total kinetic vitality of the colliding bodies before the collision is equal to the total dynamical energy of the bodies aft the hit.
In reality, almost collisions that we experience in everyday life are ne'er perfectly elastic, but collisions of smooth, hard spherical objects are nearly elastic. For these collisions, then you have,also as
Now, we leave derive a human relationship between the initial and final velocities for two bodies undergoing an elastic hit:

Law of Conservation of Linear Momentum – Resilient Collision Speed Etymologizing
i.e. the relative velocity between the 2 objects after an elastic hit has the same magnitude but the opposite direction to the relative speed between the two objects earlier the collision.
Let's immediately suppose the masses betwixt the two colliding bodies is equal, i.e. . And so our equations become
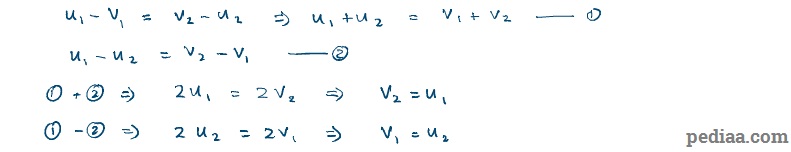
Natural law of Conservation of Linear Impulse – Velocities of Ii Bodies After an Elastic Collision
The velocities areexchanged between the bodies. Each body leaves the collision with speed of the strange body before collision.
Springless Collision – Conservation of Momentum
In inelastic collisions, the total K.E. of colliding bodies before the collision is little than their total kinetic vigor after the collision.
In completely inelastic collisions, the colliding bodies stick together after the collision.
That is, for two colliding bodies during a entirely dead collision,
where is the speed of the bodies later collision.
N's Provenience – Conservation of Momentum
A Newton's Provenienceis the aim shown below. IT consists of a phone number of spherical metal balls of equal mass in contact with each other. When any bi of balls is embossed from one side and let go, they come down and collide with the other balls. After the collision, the same number of balls rises up from the other side. These balls also go away with a velocity up to that of the incident balls just before the collision.
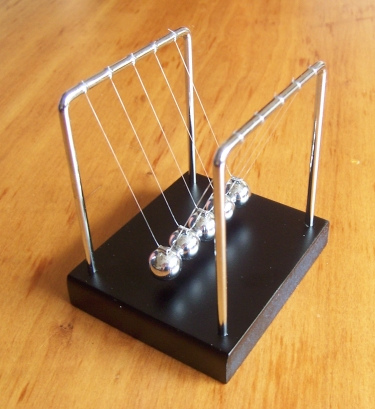
What is the Law of Preservation of Linear Impulse – Newton's Cradle
We can predict these observations mathematically, if we assume the collisions to be elastic. Guess each ball has a mass. If
is the number of balls initially raised up by a person and
is the number of balls that gets embossed as a event of the hit, and if
is the speed of incident balls upright before collision and
is the speed of the balls that get inflated up aft hit,

What is the Law of Conservation of Linear Momentum – Newton's Cradle Derivation
i.e. if we raised balls initially, the same number of balls would get raised after collision.
As the balls are raised, their kinetic DOE is converted to potential energy. Considering the conservation of vigour, then, the height that the balls get up sprouted to will be same as the height that the balls were raised to by the person.
References
Giancoli, D. C. (2014). Physics Principles with Applications. Pearson Learner Mansion house.
Image Courtesy:
"A Newton's Provenance" by AntHolnes (Own mold) [CC BY-SA 3.0], via Wikimedia Commons

what is law of conservation of momentum in physics
Source: https://pediaa.com/what-is-the-law-of-conservation-of-linear-momentum/